
15 February 2022
Demystifying Cloud Computing – Part 1: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
by Stephanie Schuldes
“The cloud“ is a collective term for various services and delivery models. This article is the first of a two-part series where we take you through the basics. Part one focuses on the service models IaaS, PaaS and SaaS. The next article will look at the deployment models Public, Private and Hybrid Cloud.
Five Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is an umbrella term for the delivery of computing capabilities and resources over a network, most commonly the internet. According to the NIST, cloud computing is defined by five core characteristics:
- On-demand self-service: Customers can gain access to computing capacity through a self-service interface without having to meet with a salesperson or sign a contract.
- Broad network access: The provided functionality is accessible via the internet and various devices.
- Resource pooling: Providers serve multiple customers at the same time (multitenancy) and dynamically adapt the assigned resources based on what the customer requires at any given time. This also means that customers are typically unaware of the exact location of the resources.
- Rapid elasticity: Resources can be scaled up and down quickly and sometimes automatically, giving the impression of limitless computing capacity that is available at any time.
- Measurable service: Resource usage is tracked, allowing for monitoring, optimization, and transparency on the part of both the provider and the customer.
Cloud Service Models
To enable a system to meet these five requirements, the task of managing infrastructure is transferred from the user to the cloud provider. There are several ways in which the responsibility for the hardware and software stack can be divided between these two parties. As a result, three cloud service models have emerged: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
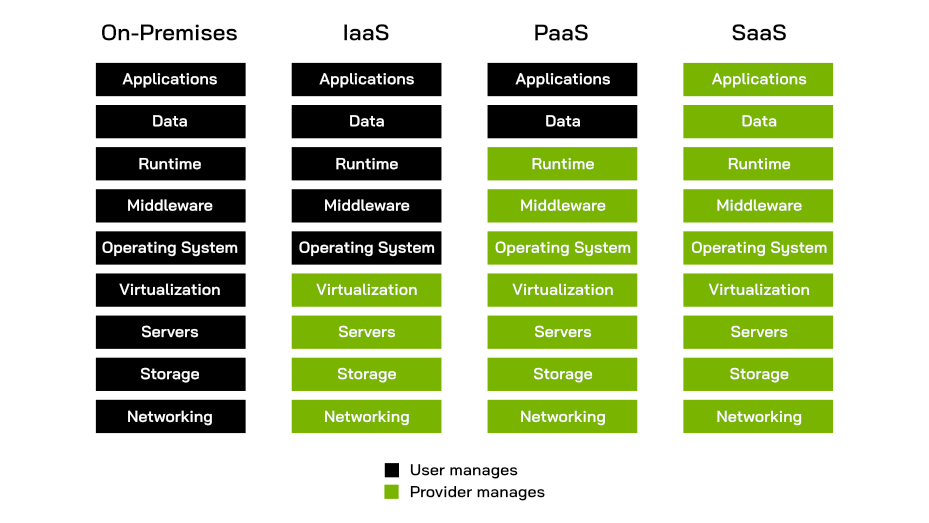
What is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)?
With IaaS, the technical infrastructure is provided by a data center (hardware, network, storage, servers). Instead of purchasing their own servers, users can rent them on an as-needed basis. The IaaS provider is responsible for maintenance. From the operating system on up, the user is in charge of everything else. In essence, users have a virtual data center.
Examples of IaaS
- Google Cloud Infrastructure
- Amazon Web Services (AWS, also PaaS)
- Microsoft Azure (also PaaS)
- IBM Cloud
- Red Hat OpenStack Platform
Use cases
- A qualified IT and development team is available.
- A high level of control over installed components is required.
- Computing capacity is required, but there are no resources for a data center of one’s own.
Advantages
- Flexibility and scalability allow resources to be quickly adapted to actual needs.
- No effort for acquisition and operation means lower costs and more time for IT staff to focus on other tasks.
- It is more cost-effective to pay only for the resources that are actually used.
- Outsourcing of backup and data-privacy responsibilities
- Convenient use
Disadvantages
- The development team has to start almost from scratch.
- Higher maintenance effort for the customer, as a larger part of the stack is in his or her area of responsibility.
- Greater reliance on the provider in terms of failure safety (infrastructure is not accessible to the customer), which may have an impact on usability and customer satisfaction.
What is Platform as a Service (PaaS)?
PaaS provides an integrated runtime and development environment (including hardware, software, and maintenance) as a service via the data center. Thus, the user pays for the use of databases, file systems, or application servers, for example. The user manages his or her own applications and data.
Examples of PaaS
- Amazon Web Services (AWS, also IaaS)
- Microsoft Azure (also IaaS)
- SAP HANA Cloud Platform
- Microsoft Azure
- Google App Engine
- Salesforce Platform
- Magento Commerce
Use cases
- As a framework for developing and running custom applications
- Analytics/Business Intelligence: (AI-supported) analysis of company data can provide new insights, better forecasts and decisions, and innovation.
- Additional services to complement and integrate existing applications
Advantages
- There is no effort (in terms of time and money) required for the acquisition and operation of infrastructure (e.g., maintenance, security updates, backups).
- In addition to infrastructure, there is readily available middleware, databases, and tools that support the development and deployment of applications of varying complexity, allowing developers to work faster, develop fewer components themselves, and retain development freedom.
- Developed applications have high scalability and availability and can be provided to a large number of customers (multitenancy).
- The platform provides a unified development environment for the entire development, testing, deployment, and updating life cycle.
- Focusing on the actual business idea leads to quick results.
- Less expertise is required, for example, to operate infrastructure or analyze data.
- More convenient development for multiple platforms
- Use of complex tools is possible for a limited time, resulting in cost savings compared to acquisition, or provides access to tools that would otherwise be prohibitively expensive.
- Even one-time use of a service becomes affordable, as there are no high costs for infrastructure of rarely used applications.
- Enables development teams to work from anywhere (also worldwide)
Disadvantages
- Less control than with IaaS
- More reliance on the provider (availability, maintenance, security, data protection, support)
- Data privacy protection concerns must be addressed.
What is Software as a Service (SaaS)?
With SaaS, complex software is made available via the data center. Instead of a one-time license purchase and local installation, the software is provided as a service (similar to buying vs. renting a car). This trend has been aided most by web services, which are typically billed on a per-call basis.
Examples of SaaS
- Microsoft 365
- Trello
- Slack
- Google Workspace (e.g., Gmail)
Use cases
- As an end user, direct use of applications (either for business-related tasks or to create additional websites and applications)
- As a developer, deploying applications to multiple end users
Advantages
End users
- Subscription-based fees are flexible.
- No installation and maintenance effort for end customers
- Responsive and/or accessible designs are more available because of browser-based interfaces.
Developers
- Lower operating costs through multitenancy: The application can serve multiple customers from a single system instance.
- Updates and fixes are distributed more quickly (only needs to be done in one instance and immediately available to all clients).
- Diversification and innovation: rapid development and monetization of new applications, resulting in access to new customers
Disadvantages
End users
- Because there is no access to the code, there are often few customization options.
- Requires an internet connection
- Availability, maintenance, security, privacy, and support are all dependent on the provider.
Developers
- Responsible for availability, maintenance, security, privacy, and support
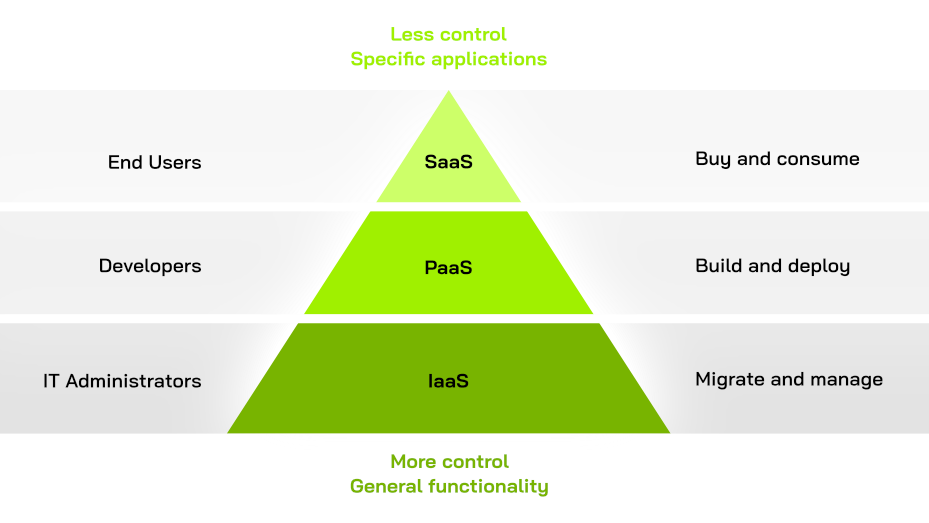
IaaS, PaaS, SaaS – which Model is Right for your Project?
Every organization must decide which methods are best to use in the development process. Projects with limited resources and a focus on simple applications, processes, or platforms can save a lot of time and money by developing exclusively in the cloud. For most applications, organizations that value flexibility, performance, security, and portability benefit from the hybrid combination of cloud and existing on-premises infrastructures.
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS all provide distinct advantages to businesses in terms of scale, performance, and cost savings. IaaS, for example, is ideal for organizations looking for quick deployment cycles from a scalable system. PaaS retains infrastructure control while removing much of the back-end work typically associated with developing and maintaining applications. Finally, SaaS enables businesses to quickly and easily access new applications, as well as regular access to new features and upgrades.
Part 2 continues with the cloud deployment models Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud.
You might also like
Do you have any further questions?



